How to Talk Experimental Film: A User’s Guide

As a medium, film is unique because it captures life in a way that cannot be captured through other forms of art, like painting or photography. Film is able to represent time, its duration, and motion, which brings it the closest to capturing life itself. Even the most conventional, mainstream film or video is able to accomplish this captivating feat. (If you beg to differ, notice what happens when there’s only one moving image in the room.) Experimental films not only capture or represent life, but also challenge the form and content of filmmaking and its conventional patterns, in order to provoke and, at its best, transcend how we compose our lives on and off-screen.
So what qualifies as experimental?
A video opens with a unique score of digitally-manipulated industrial sounds mixed with a distorted version of a familiar pop tune, the 1997 teenage anthem, “Kiss Me” by Sixpence None the Richer. A jaundiced character with glowing cat eyes giggles in the pitch of a crazed raccoon. She drives happily through cyberspace, looking in wonder at the digital snowflakes floating across the screen. That’s the opening of Ryan Trecartin’s 2007 “I-Be Area (Pasta and Wendy M-PEGgy)”. Or how about the genre-bending and taboo-ignoring film “Palindromes” by Todd Solondz? The conceptual film centers on a 13-year-old protagonist named Aviva (notice, her name is a palindrome), who is played by eight different actors of varying races, ages, and genders. The film is a dark, fearless, and unblinking look at teenage sexuality through multiple voices and vantage points: a fragmented look at a modern-age identity crisis.
Within the broad genre of experimental film, there emerge at least two different types of players: filmmakers who experiment with form and narrative content, and artists who use film or video as a medium through which to express their vision. This distinction between filmmakers and artists is not to say that filmmakers can’t be considered artists, or that artists can’t be considered filmmakers. In fact, the lines are not always clearly defined. I myself struggle with how to identify myself: filmmaker or artist (or both)? And in reality, my primary mode of identification varies depending on the particular context.
However, it’s important to understand that experimental film isn’t a simple or singular catchall. There’s a spectrum of people who create experimental films for different reasons. The results are excitingly diverse and varied and for that, The Independent thought it would be helpful to check in with someone working in the medium, me, for an introductory grasp on terms and definitions:
EXPERIMENTAL FILM
For me, experimental film is essentially a broad stroke or umbrella term for moving images that explore the human condition, nature, or fantasy in ways that haven’t been traditionally explored before. “Experimental film” includes a wide range of works, from a video performance of a heavily made-up woman smearing her face on a pane of glass (Pipilotti Rist, “Be Nice to Me“) to Wes Anderson’s “Moonrise Kingdom“. These are films in which filmmakers and artists are experimenting with the form (think jump cuts, overlays, the use of text on screen, films that use both animation and live-action) or content. Let’s keep in mind that most filmmakers aren’t experimenting the way scientists are, with the use of the scientific method that we all learned back in our middle school days. But we do know that they’re playing with (some quite methodically and others more freely) and therefore expanding the genre. Their intent isn’t to continue in the way mainstream films have been made. Instead, they want to challenge it.
Of course, the scope of experimental film is quite broad. Some films dabble in experimentation, with one camera angle or a topic that’s taboo or unconventional. Other films really push the boundaries, so much sometimes that we can’t even really decide if it is a film or not.
AVANT-GARDE FILM
I’m probably not alone in thinking of art critics in a gallery with affected intonations when I think of the term “avant-garde.” The term itself, before it was applied to art, was a military term that literally means “forward guard.” It described the soldiers on horseback that led troops into battle. They were on the front line of troops to go out and face the enemy.
Forgive the metaphor, but avant-garde filmmakers are those original soldiers on horseback. They’re first. They’re fearless. And their films usually aren’t well received by the general public. Avant-garde films are wholly experimental, pioneering films: films that after you’ve seen, you turn to friends and ask with wide eyes, “What was THAT?” These are the types of experimental films that a lot of people have a hard time digesting. They can be confusing, strange, grotesque, and purposefully disjunctive. And that’s okay. Because avant-garde films aren’t crowd-pleasers. The filmmakers creating those works know that.
It is important to note that “avant-garde film” was a term first used to describe Dadaist and surrealist films of the 1920s. A film that’s still widely regarded as one of the most avant-garde films in history is Luis Buñuel and Salvador Dalí’s 1929 film, “Un Chien Andalou“. The film opens with a man causally sharpening a straight razor on a piece of wood. Wagner’s powerful, imposing score drives the action forward. Cigarette smoke unfurls as he concentrates on his task, glancing at the moon. The man opens the eyelid of a calm woman and slices her eyeball in half with the straight razor. The moon is temporarily spliced in half by the horizontal movement of a stray cloud. The woman’s eye spits out a gelatinous substance.
In the 21st century, we hear all the time that in art, “nothing is new.” As an artist, I can’t (and won’t) wholeheartedly agree with that statement. However, I will acknowledge that as modern filmmakers or film viewers, we have a relatively long history. If I were writing this article in the 1920s, I could give you tons of examples of what’s called “avant-garde film,” and every film would be shockingly novel. It’s a little harder now: as a society, we have seen more films, we reference more films, we pay homage to more films, and we borrow from more films. So, it’s important to also consider that avant-garde is a term steeped in chronology. What was once avant-garde may now be the most popular film type.
Take for example the most commonly cited “influential film” for filmmakers: “Citizen Kane” by Orson Welles. When this film first came out, it was monumentally innovative for its time: the use of the newsreel, the death of the protagonist in the first scene, the unreliable narrator, the signifiers, the ambiguous sound, the deep focus…and the list goes on. The thing is, today’s unguided audiences probably wouldn’t be able to distinguish Citizen Kane as an innovative, avant-garde film, which it was for its time.
So I suppose that begs the question, what is avant-garde film today? Funny enough, it’s mostly likely seen in museums and galleries…yes, the beacons of affected intonations. But it’s true. Current avant-garde films are less likely to be exhibited in a movie theater because the form does not prioritize the viewing experience of the audience in the way that commercial films do. Museums and galleries (sometimes) allow for flexibility: artists and filmmakers can make space another dimension that the viewer must experience, which is why avant-garde often intersects with the realm of video installation.
UNDERGROUND FILM
“Underground film” is a term that was coined in the 1960s and is still used today, though certainly without the same connotation. You can see the term in the film festival circuit: the Boston Underground Film Festival, New York Underground Film Festival, Chicago Underground Film Festival…and so on.
To be honest, though, the term is a bit antiquated. It may evoke images of cigarette smoke, black and white super 8 films, or the purr of a film projector. However, I don’t see it used much in a modern context except in the titles of those film festivals or as a bit of a joke. And perhaps it’s because there really isn’t much of a true underground film scene anymore. This makes sense because when the term “underground film” first became popular in the 1960s, it described a film that was forced to be made with some sort of secrecy. Sheldon Ren, author of “An Introduction to the American Underground Film“, writes that the term came into usage because “there was at the time a feeling that the forces that be were trying to keep this certain kind of film from being made. Underground described an attitude: the determination that films should be made and should be seen despite all economic and legal barriers.”
While budget constraints are still a very real challenge for modern filmmakers, having a film be seen is not as problematic. The Internet and all the available viewing channels, even specific channels made for people who appreciate experimental film, eliminate the barriers filmmakers faced a few decades ago. The Internet, after all, in most nations anyway, is public. So in an era when we as a society can’t (or perhaps won’t) hide anymore or operate in true secrecy, underground film doesn’t carry the same bite.
Of course…unless we’re talking about banned films, like Todd Haynes’ “Superstar: The Karen Carpenter Story“. The 43-minute film re-enacts the story of musician Karen Carpenter, who tragically died of anorexia, with a cast made up entirely of Barbie dolls. It was released in 1987 in film festivals, but was recalled when Haynes lost a lawsuit regarding the music licensure in the film. As a result of the lawsuit, the Carpenter estate has required that all copies of the film have been recalled or destroyed. So, if you happen to find a copy of the film and share it with someone else, that would certainly be an experience in the vein of underground film. (I dare you.)
While instances like Superstar are rare in the United States, the spirit of underground film is still alive because of the money issue. Funding is little and budgets are tight for filmmakers (and the arts in general), so many still carry on that attitude, or even write into grant proposals, “this film will be made no matter what.” Lots of filmmakers are putting together crews that work for free, working long and impossible production hours, and doing everything and anything to get a film made, even if it means bankruptcy or begging for money. Scrappy, pull yourself up by your bootstraps, DIY-style filmmaking is actually more popular than not. In fact, some might argue that the underground film attitude of the 1960s is perhaps the spirit of independent film today.
VIDEO
As a term and a medium, “video” tends to be more elastic and flexible than “film.” Videos can range from recorded performances (also known as video performance), to short movies (which can also be referred to as “short films”), to sculptural works that include moving images (also known as “video installation” or “new media installation”) to moving images that are digitally recorded as opposed to chemically processed. Video can challenge conventions of exhibition as well. For example, movies or “films” are conventionally made to be watched in theaters. (Whether or not they are being watched in theaters nowadays is another topic). Videos, on the other hand, can demand to be exhibited in alternative ways, such as in video or new media installations, where the display space is an important part of the experience.
VIDEO ART
“Video art” is a really flexible genre, and its ambiguity is a gift for experimental artists. It’s an art that uses the moving image as its medium. Instead of paint, video artists use the camera and the technology’s unique qualities. The canvas is the screen. The term is broad and can reference anything from a tightly edited short film with a beginning, middle, and end, to one that has none of those typical narrative guideposts (or even end credits for that matter) to a filmed performance in which an artist walks around a square in an exaggerated manner (a Bruce Nauman piece, aptly titled “Walking in an Exaggerated Manner around the Perimeter of a Square“). And of course, video art catches all other video pieces that lie between the spectrum of a short film and video performance, such as music videos.
I personally love video art as a genre because it allows me to do things that films can’t do, like experiment with the idea of modularity and singularity. Last year, my creative partner Danny Roth and I produced an experimental video project, titled “7 d.a.y.s.“, in which we conceived, produced, and edited one video a day for seven days. The project grew out of a fascination with the ephemeral and the fleeting beauty of the creative idea. Each video was themed and named for the day on which we created it. Themes included memory, art&madness, city, trance, spinning, senses, and nature. The intention of the project wasn’t to create seven perfect, whole films, but to capture a week’s worth of creativity on video. The videos are meant to be impulsive, visceral, fleeting. In addition, we also wrote poetry and text for each of the videos because, for me, words and the act of writing are as integral to my life as visuality. One interesting thing to add here is how I term my work. The title is 7 d.a.y.s., but what I use as the subtitle varies from time to time. Sometimes I call it “an experimental film project,” other times I call it “an experimental video series,” and others, I call it “a conceptual film project.” This just goes to show the elasticity of these genres and how they can overlap and intersect with each other.
VIDEO INSTALLATION
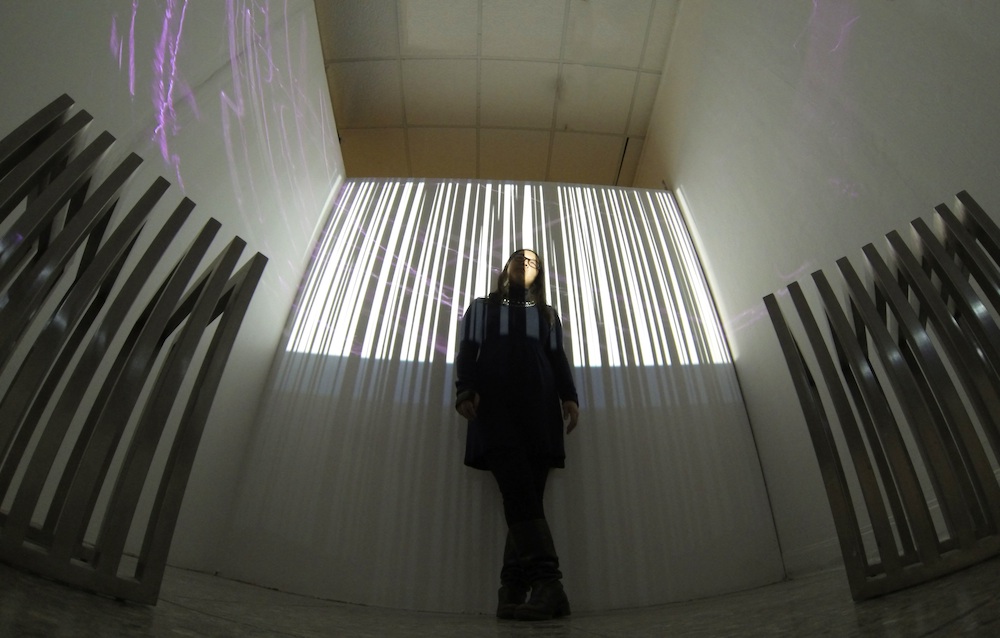
The term “installation” is another flexible term. It’s a word used to describe works that use space as an additional dimension in a work of art. Installation pieces are often sculptural in that they activate and consider space. “Video installation,” then, describes works that activate space with video. A prime example of a video installation is American artist Tony Oursler’s work, where video projection is a key element. Oursler innovatively moves the viewing space away from the big screen, or little screen, and onto unconventional surfaces. He might project video of faces engaged in monologue or dialogue with the audience onto stuffed bodies, or bedroom scenarios (the space under a bed), for example. I’d say that it’s the moving image in his works that shocks, awes, and inspires audiences. “Little Worlds“, a collection of Oursler’s work is currently exhibiting at the Honolulu Museum of Art until June 23, 2013.
Despite the device on which a moving image was created and what term is used for it, what makes a film (or video) experimental is the unconventionality of its form or content. These kinds of films allow the audience to see and experience the world in a way that they’ve never seen or experienced before, through uniquely calibrated eyes. The process may shock us, amaze us, or disturb us. Most experimental filmmakers and artists I know are shooting for all three, plus a quality or two that defies articulation.